SavedState Compiler Plugin
Kotlin compiler plugin generates support methods for use SaveStateHandle without constants and string variables.
Example
If need to use SaveStateHandle, you must declare a variable, like that:
companion object {
private const val TEXT_FIELD = "text"
private const val PASSWORD_FIELD = "password"
}
val text: MutableLiveData<String> = savedStateHandle.getLiveData(TEXT_FIELD, "Hello World")
val password: String
get() = savedStateHandle[PASSWORD_FIELD]
This plugin eliminates necessity declares a variable. Same example with plugin:
@SaveState
val text: MutableLiveData<String> = getTextLiveData("Hello World")
@SaveState
val password: String
get() = gePasswordValue()
How it use
- Apply plugin to your module, sync it and you can use annotation
@SaveState - Mark by this annotation fields witch you want to use with SavedStateHandle, and support methods generated in realtime.
Importance:
- The SaveStateHandle variable mast be declarated in class.
- As a key for SaveStateHandle plugin uses name of a annotated variable
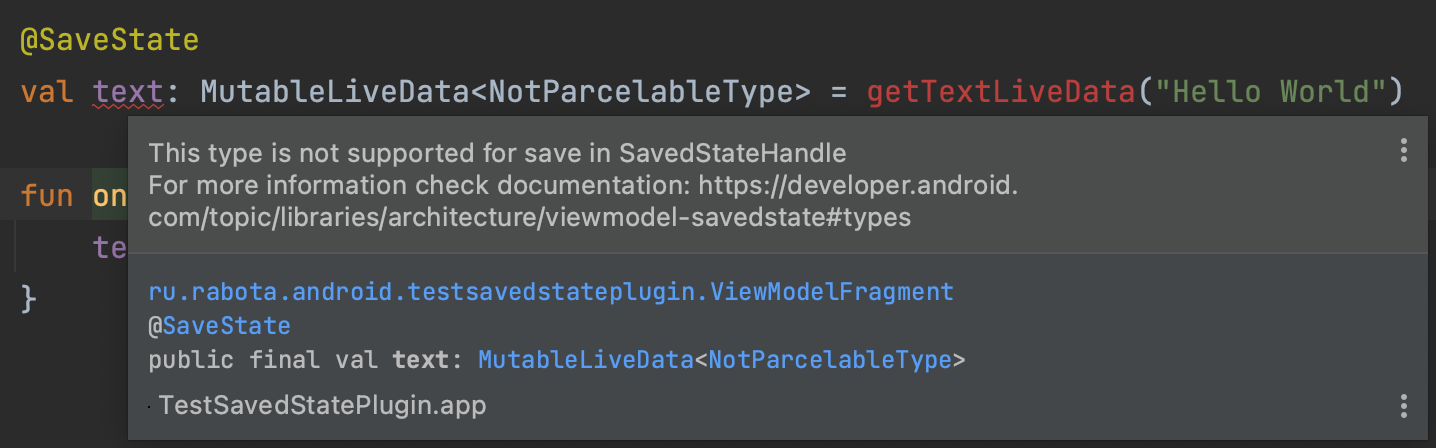
- Supported variable types are listed here. Also, all these types can be specified as a generic param in LiveData or MutableLiveData
4 generated methods
For example takes this variable
private val savedStateHandle: SavedStateHandle
@SaveState
val text: LiveData<String>
1. getTextValue()
It method return value from SavedStateHandle. Inside it:
private fun getTextValue(): String? {
return savedStateHandle.get<String>(key = "text")
}
2. getTextLiveData()
It method returns LiveData from SavedStateHandle. Inside it:
private fun getTextLiveData(default: String? = null): MutableLiveData<String> {
return savedStateHandle.getLiveData<String>(key = "text", initialValue = default)
}
3. getIdentifierText()
It method returns the key witch uses for set and get value in SavedStateHandle. Inside it:
private fun getIdentifierText(): String {
return "text"
}
4. setTextValue()
It method sets value in SavedStateHandle. Inside it:
private fun setTextValue(text: String?) {
savedStateHandle.set<String?>(key = "text", value = text)
}
One more things
The plugin also allows:
1.Type checking. Supports all types from the documentation and indicates an error if, for example, class did not implement parcelable
- Validates presence of a variable SavedStateHandle in a class. If class contain an annotated variable and the variable SavedStateHandle is not found in the class, then the plugin will notify you
Installation
- In project-level
build.gradle:
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
// Or
gradlePluginPortal()
}
dependencies {
classpath "io.github.toxa2033.saved-state:gradle-plugin:1.0.5"
}
}
- In module-level
build.gradle:
// For each module that needs to use the annotations
apply plugin: 'io.github.toxa2033.saved-state'
//or
plugins {
id 'io.github.toxa2033.saved-state'
}
dependencies {
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-savedstate:$lifecycle_version"
}
IDE Support
- Install the IDEA plugin
- Launch the IDE and open plugin settings (Preferences -> Plugins -> Marketplace)
- Search for "SavedStateHandle Kotlin Compiler" and click install
Versions
| Kotlin Version | Plugin Version |
|---|---|
| 1.5.30 - 1.6.21 | 1.0.* |
License
Copyright (C) 2022 Toxa2033
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.